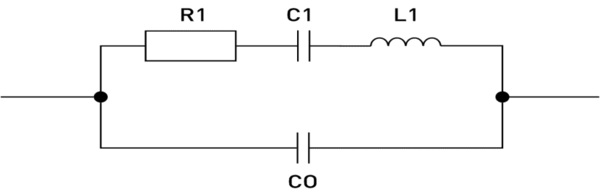
Components and significance
- R1 (Resistance = technical term: Resonance Resistance)
- Models the losses in the crystal (mechanical damping, conduction losses).
- Typical: a few ohms to a few hundred ohms for MHz crystals. kOhm for kHz oscillating crystals
- C1 (capacitance = technical term: motional capacitance)
- Corresponds to the elastic restoring force in the crystal.
- Typical: a few fF to pF (femto- to picofarad)
- L1 (inductance = technical term: motional inductance)
- Represents the mass inertia of the oscillation (mechanically: inertia of the crystal).
- Typical: a few mH (millihenry)
- C0 (parallel capacitance = technical term: shunt capacitance)
- Represents the electrical capacitance between the connections of the quartz (e.g. through the electrodes).
- Typical: 1 - 7 pF depending on the quartz crystal
It would therefore be possible to generate a frequency by constructing a circuit consisting of L1 + C1 + R1 with a parallel capacitance C0. However, this frequency would be very inaccurate. The circuit itself is complicated to construct and expensive to assemble. Our highly innovative oscillating crystals, on the other hand, are very precise, extremely durable and cost-efficient.